Treating Dental Cavities

Cavities and dental decay are prevalent health issues worldwide. Basic Health Research data shows about 90% of Indonesians have experienced it. Do you remember how it was?
When you were a kid, your parents might have told you, "Watch out, caterpillars will eat your teeth!" to get you to quit eating sweets. Is it true, however, that there are caterpillars in our teeth that cause cavities? Let's find out ….
Cavities are damaged portions of the tooth's hard surface caused by a small hole. If the small hole is not repaired, it will expand and affect the deeper layers of the tooth, resulting in severe toothaches, infections, and even tooth loss.
So, what exactly causes cavities or tooth damage? There are many things, but if you enjoy eating something sweet and do not brush your teeth afterward, you have a problem.
This propensity of "damaging" teeth is exacerbated by a bacterium in the mouth called Streptococcus mutans. Plaque arises from the bacteria producing acid from all sweet foods entering the mouth.
Without appropriate tooth brushing, plaque acids destroy the minerals in tooth enamel (the outer layer of teeth consisting of calcium and phosphate), leaving tiny holes in it. Minor damage extends to the dentine layer beneath the enamel, revealing a cavity (hole). The white spot turned a light brown tint. The deterioration of teeth begins at this point.
If the damage is not treated, it spreads to the dentin, the layer beneath the enamel. This layer is significantly softer than enamel. Cavities in the teeth will grow faster if plaque and bacteria reach this layer. Your teeth become more sensitive when you eat anything sweet, hot, or cold. Previously, white spots became darker brown.
If this layer is destroyed, the infection travels to the pulp, the tooth's deepest layer. The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels that carry nutrients to the tooth and keep it alive. You will experience discomfort if the decay reaches the pulp of your tooth. The gums around the teeth become red and inflamed. Spots on the teeth turn dark brown or black.
An infection will develop if the lowest layer is damaged and not addressed. A pus pocket is near the tooth's root end (periapical abscess). Symptoms may include pain radiating to the jaw or face.
You currently have edema in your face and lymph nodes in your neck. A dental abscess has spread to adjacent tissues and other body parts. In rare situations, the infection might spread to the brain or bloodstream (sepsis).
You may wonder how your teeth can still have cavities when practicing good dental hygiene and consuming a healthy diet. Aside from those two factors, other factors raise the chance of cavities. Here they are.
- Dry mouth (xerostomia). Certain conditions (such as Sjögren's syndrome) or medications (such as antidepressants) put you at risk for dry mouth.
- Family history of tooth decay.
- Gum recession.
- Radiation therapy to treat head and neck cancer.
- Suffer from anorexia or bulimia.
- She was suffering from gastric acid reflux disease (GERD).
Cavity Treatment
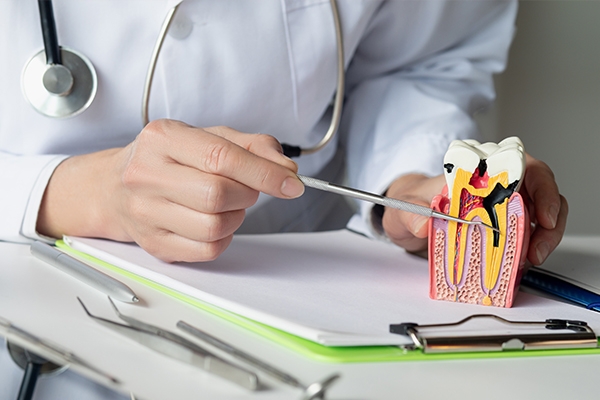

What if the teeth already have cavities? Is it still necessary to treat it? Yes, cavities must be treated to avoid complications. Some actions that can be taken include:
1. Fluoride treatment
Fluoride treatment restores the damaged enamel in the early stages of tooth decay, a process known as remineralization. This procedure helps correct early indicators of cavities.
2. Fillings for teeth
After cavities, the dentist drills out the deteriorated tissue and replaces it with fillings. Dental fillings are composite resin (a tooth-colored substance) and silver or gold amalgam.
3. Root canal therapy
Root canal therapy relieves pain caused by advanced tooth decay. Endodontists (specialists who treat tooth root problems) commonly remove the dental pulp before filling the canal and pulp chamber with gutta-percha (a specific filling material). Dental crowns are occasionally required to reinforce diseased teeth.
4. Pulling teeth
If root canal therapy is not an option, tooth extraction is another option. You may require a dental bridge or implants to replace the extracted teeth.
You're what you eat

We should have a well-balanced diet rich in nutritious foods to keep our teeth healthy. For example,
1. Dairy products
Milk, yogurt, and other dairy products can help improve tooth enamel. Its high calcium and protein content can help battle the causes of cavities. A lack of calcium increases the risk of tooth loss.
2. Nuts
Almonds are a low-sugar nut that is high in fiber and calcium. Eating almonds will help build the enamel.
3. Vegetables
Green vegetables, such as spinach, edamame, lentils, and asparagus, are high in folic acid. This chemical is beneficial for strengthening enamel, avoiding gum disease, and lowering inflammation.
4. Onion and garlic
Besides being delicious, shallots and garlic are also good for your teeth. Both effectively reduce the germs responsible for gingivitis, dental decay, cavities, and foul breath.
5. Salmon
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and cod. Improves gum repair after infection.
6. Apples and strawberries
Strawberries can be used to eliminate tooth stains. Its ellagic acid content can whiten teeth.
To keep your teeth healthy into old age, combine these crucial things: good eating and regular teeth cleaning after eating. Make sure to have your teeth checked at least twice a year.
Remember to check your teeth at least twice a year at GWS Medika Clinic, a dental clinic in Jakarta Selatan. At this Permata Hijau dental clinic, you can also do various dental treatments, such as scaling and bleaching, root canal treatment, and extraction.