Super Flu: A New Flu Variant?

More severe symptoms than the common flu, along with the rapid spread of the virus, have drawn health experts’ attention to cases of what is known as super flu.
In Indonesia, as of the end of 2025, 62 cases of a new flu variant, referred to as the super flu, have been recorded.
Its transmission rate is relatively high, with one infected person potentially infecting two or more others.
Super flu is caused by a variant of the Influenza A (H3N2) virus, subclade K, which was first identified around June 2025.
This variant spreads quickly, triggering simultaneous increases in cases across multiple countries.
Super flu is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
The virus can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces and enter the body when hands touch the nose, mouth, or eyes.
Transmission is more likely in enclosed, crowded spaces, such as public transportation, offices, schools, or healthcare facilities.
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing severe symptoms or complications from super flu, including:
- older adults (aged 60 years and above);
- children;
- pregnant women;
- people with chronic diseases (such as diabetes, heart disease, asthma, or lung disorders);
- individuals with weakened immune systems.
How is it different from the common flu?

Symptoms of super flu generally appear suddenly, 2–3 days after exposure to the virus.
At a glance, they may resemble those of the common flu. However, the symptoms tend to be more severe, last longer, and significantly interfere with daily activities.
Symptoms of super flu that should be closely monitored include:
- high fever up to 39°C–40°C;
- persistent dry cough;
- severe headache;
- runny nose;
- muscle and joint pain;
- chills;
- extreme fatigue;
- reduced appetite;
- eye discomfort, such as pain, watery eyes, or light sensitivity.
In children, super flu symptoms are often more nonspecific and may be accompanied by additional complaints, requiring closer monitoring.
In contrast, the common flu usually affects the upper respiratory tract and causes milder symptoms.
People with the common flu are generally still able to carry out light activities and rarely experience severe or prolonged symptoms, unlike those who may experience them with Influenza A (H3N2) subclade K infection.
Preventive measures against super flu
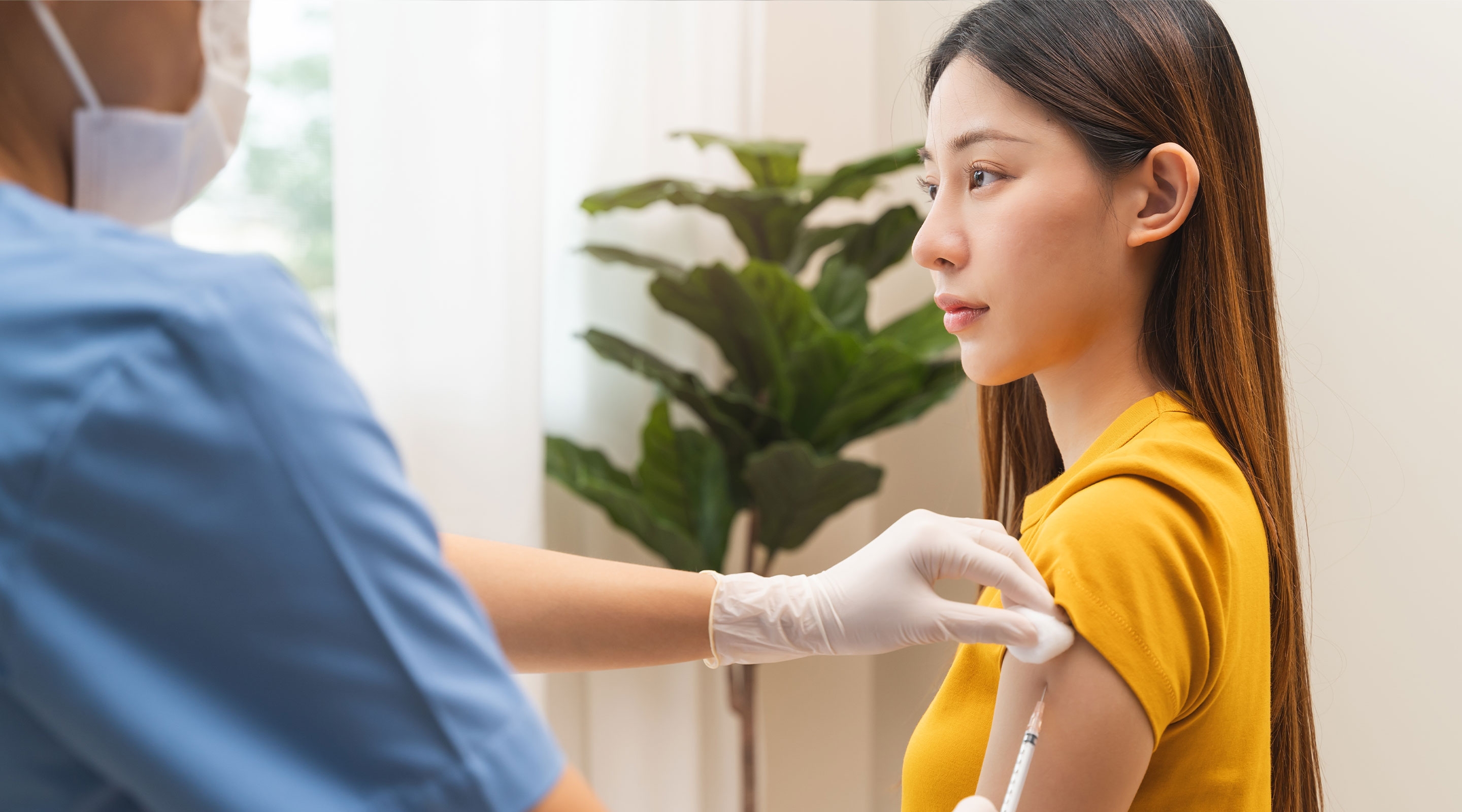
1. Influenza vaccination
Influenza vaccination remains the primary recommended preventive measure against super flu.
It is strongly advised for high-risk groups, such as older adults, pregnant women, and individuals with underlying medical conditions.
In addition to helping prevent infection, influenza vaccines have been shown to reduce symptom severity and the risk of complications if infection does occur.
2. Consuming nutritious foods
Nutritious food intake plays an important role in maintaining the immune system so it can effectively fight viral infections, including super flu.
A balanced diet helps the immune system function optimally and supports recovery when the body is exposed to viruses. Essential nutrients that support immunity include:
- Protein
Needed for antibody production and tissue repair. Sources include fish, eggs, lean meat, tofu, tempeh, and legumes. - Vitamin C
Acts as an antioxidant and helps enhance immune response. It is found in oranges, guava, kiwi, strawberries, and green vegetables. - Vitamins A and E
Help maintain the health of cells and tissues, including the respiratory tract. Sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, avocados, and nuts. - Zinc and other minerals
Play a role in immune system function and help speed up recovery. Zinc can be found in meat, seafood, seeds, and dairy products. - Adequate fluid intake
Helps prevent dehydration, maintains moisture in the respiratory tract, and supports overall body function.
3. Clean and healthy lifestyle practices

Practicing clean and healthy habits plays an important role in reducing the risk of virus transmission, including:
- washing hands regularly with soap;
- wearing a mask when feeling unwell;
- practicing proper cough and sneeze etiquette;
- ensuring adequate rest;
- Consuming balanced nutrition;
- exercising regularly.
A combination of vaccination and healthy lifestyle habits is key to protecting yourself and those around you from super flu.
When should you see a doctor?
Seek medical attention immediately if you experience:
- a high fever that does not subside for more than three days;
- shortness of breath or chest pain;
- extreme fatigue that makes daily activities difficult;
- decreased consciousness or confusion;
- worsening symptoms despite rest and medication.
Protect yourself and your family with influenza vaccination and a healthy lifestyle.
Visit GWS Medika Clinic in Jakarta if your flu symptoms are more severe than usual.



