Oral Contraceptives: Benefits and Risks

In the past few months, Nirina has been using birth control pills to prevent conception. Since then, she has often experienced headaches and terrible acne, and her hair has begun to fall out. Sometimes, she has spotting (light bleeding outside of her menstrual cycle). What exactly was Nirina's experience? Let's read more.
Birth control pills are a type of hormonal contraceptive. The hormones in these pills not only prevent ovulation but also prevent fertilized eggs from attaching to the uterus.
Some types of hormonal contraceptives also make the mucus in the cervix (uterine opening) thick and sticky, making it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
Birth control pills are up to 99% effective in preventing pregnancy when taken regularly every day. In addition, these pills contain hormones that help regulate the menstrual cycle, reduce PMS symptoms, lower the risk of ovarian and uterine cancer, treat acne, and help treat endometriosis.
However, the effects of hormonal contraception can vary from person to person. Although it provides many benefits, some users can also experience side effects like Nirina.
1. It affects the reproductive system
Women's ovaries naturally produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Both of these hormones can be synthesized and used in birth control.
Higher than normal levels of estrogen and progesterone can prevent the ovaries from releasing an egg. Without an egg, sperm have nothing to fertilise. Progestin also changes the texture of cervical mucus, making it thicker, stickier, and more challenging for sperm to reach the uterus.
2. Reduces menstrual cramps
Using specific hormonal birth control methods, such as the hormonal IUD (which contains the hormone progestin), can make your periods lighter and shorter. It can also reduce menstrual cramps and premenstrual symptoms.
Some types of hormonal birth control can significantly reduce menstrual pain. For examples:
3. Reduced risk of cancer
Using hormonal contraceptives may also reduce the risk of endometrial, colorectal, and ovarian cancers, even after stopping use.
However, it is essential to note that hormonal contraceptives may increase the risk of breast and cervical cancer in women who use oral contraceptive pills.
Like all medications, hormonal contraceptives have different benefits and potential risks for each person. Side effects can vary, and it is crucial to consider these before deciding to use them. For example
1. Spotting between periods

While birth control has many benefits, it can also cause side effects. Spotting between periods, or spotting, is common.
It is more common in users of deficient and low-dose hormonal birth control, such as hormonal IUDs, implants, and birth control pills. Birth control can also cause other side effects on the reproductive system, including
- irregular periods, such as amenorrhea (no periods) or extra bleeding
- vaginal irritation
- breast tenderness or breast enlargement
- weight changes
These side effects can vary from person to person. If you are experiencing any discomfort or bothersome symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
2. Cardiovascular problems

For some women, birth control pills and patches can raise blood pressure. The extra hormones in birth control can also increase the risk of blood clots.
While these side effects are rare, when they do occur, they can be severe. That's why hormonal birth control methods require a doctor's prescription and regular monitoring to make sure they are safe to use.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, contact your healthcare team immediately:
- chest pain
- difficulty breathing
- severe headache that comes on suddenly
- sudden pain in the back or jaw accompanied by nausea, difficulty breathing, or sweating
- Regular monitoring and consultation with your doctor are essential to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
It is crucial to monitor these symptoms and consult a healthcare professional if any changes are bothering your health.
3. Mood swings

Some women may experience mood swings and depression while using hormonal birth control.
As the body tries to maintain its hormonal balance, the extra hormones from birth control might cause disruption, potentially triggering mood swings.
4. Headaches and migraines
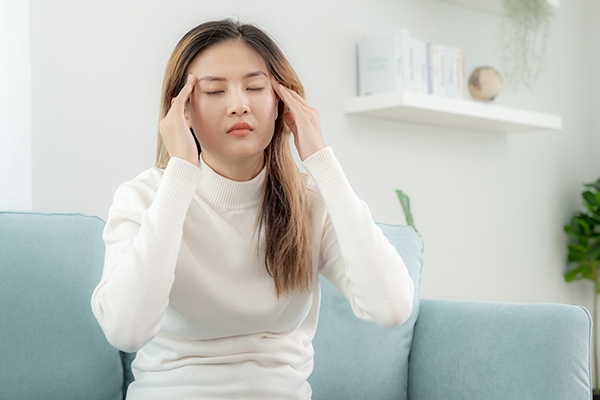

For women who frequently experience migraines, the estrogen in birth control can make migraine attacks worse.
5. Weight changes
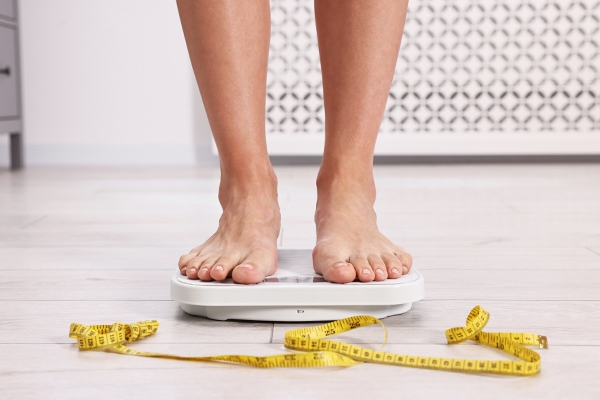

In some people, using the birth control implant and shot can cause weight gain.
Some women experience changes in appetite and weight when using hormonal birth control. However, research shows that the pill, patch, ring, and IUD are unlikely to cause weight changes.
6. Nausea
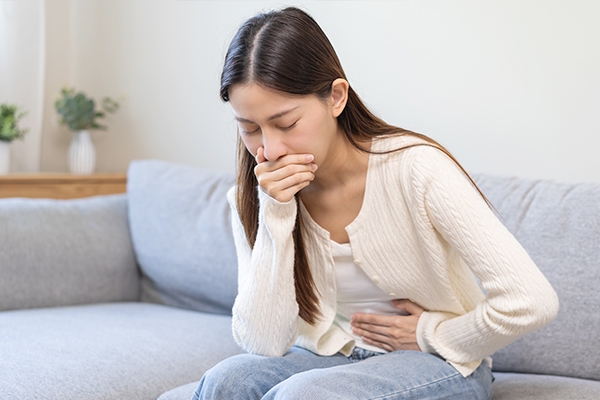

Some women who use hormonal birth control may experience side effects, such as nausea and bloating. These side effects usually subside after a few weeks as the body gets used to the extra hormones.
Taking the pill with food may help with nausea. Switching to a pill with less estrogen may also help.
However, if you experience severe pain, vomiting, or signs of serious illness, such as yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), dark urine, or light-colored stools, see your doctor immediately, as these can be signs of severe side effects.
7. Acne
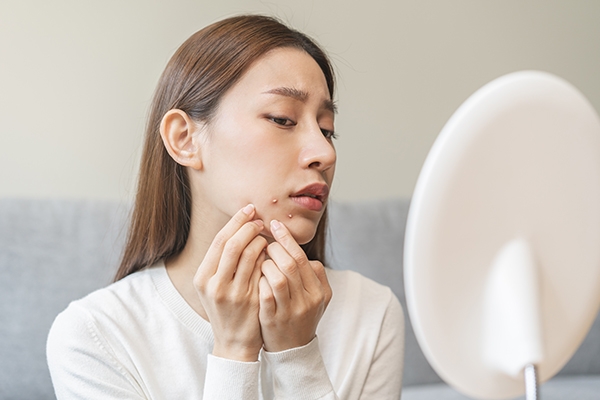

For many women, birth control can help with acne. However, some users may experience acne or not notice any changes. Because everybody's hormone levels are different, the side effects of hormonal birth control can vary and be difficult to predict.
8. Hair growth
Sometimes, the hormones in birth control can trigger unusual hair growth. More commonly, however, birth control can help to treat unwanted hair growth. Oral contraceptive pills are even one of the main treatments for hirsutism, a condition that causes coarse, dark hair to grow on the face, back, and stomach.
9. Vaginal discharge
Changes in vaginal discharge may also occur while taking birth control pills. This change can include increased or decreased vaginal lubrication, as well as changes in the texture or amount of discharge.
While these changes are usually harmless, changes in the color or odor of vaginal discharge can be a sign of infection and should be checked out by a doctor.
**
Birth control pills contain hormones that can affect the body. Side effects can vary from woman to woman, depending on the condition of the body and the type of pill consumed. However, these side effects usually subside within 2-3 months after use.
If the side effects are severe, interfere with daily life, or last more than 3 months, you should talk to your healthcare provider about a different method of contraception.
You can also consult about this problem or discuss appropriate contraception by visiting the GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta. Our medical team will be happy to help you choose the right contraception.