Itchy Intimate Area? Here’s How to Prevent It

Have you ever felt that your intimate area gets sweaty and develops an unpleasant odor easily? That’s normal. This part of the body has sweat glands similar to those found in the armpits. When sweat mixes with bacteria, it can cause an unpleasant smell and itching that feels uncomfortable.
Itching in the vaginal area is a common condition experienced by many women. The causes vary, ranging from fungal, bacterial, or viral infections to chemical exposure, allergic reactions, or hormonal changes during menopause.
These conditions can cause mild to severe vaginal itching and are often accompanied by other symptoms such as discharge, sores, rashes, or a burning sensation.
You may be able to relieve vaginal itching through self-care, including avoiding certain products and maintaining good hygiene, such as wearing breathable clothing. However, some causes, like bacterial infections, require medical treatment.
It’s essential to avoid scratching the itchy area, as it can irritate the skin around the genitals.
In most cases, vaginal itching is harmless and may subside within a few days. However, if the discomfort is severe, doesn’t improve, keeps recurring, or comes with other symptoms such as abnormal discharge, it’s best to consult a doctor.
Causes of itching in the intimate area

There are several factors that can trigger itching in the intimate area. Some are mild, while others may require medical attention. Here are the most common causes:
1. Bacterial infection
This occurs when the balance between good and bad bacteria in the vagina is disrupted.
Symptoms may include a fishy odor and thin, greyish or whitish discharge that causes itching. It’s most common in women between puberty and menopause.
2. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as trichomoniasis, genital herpes, or chlamydia, can cause itching, pain, sores, or abnormal vaginal discharge.
3. Certain skin conditions
Vulvar dermatitis and eczema are among the most common causes of genital itching. The vulvar skin may appear red, inflamed, scaly, or dry.
Scratching can lead to thickened skin, known as chronic lichen simplex.
4. Irritation or allergic reaction
The skin in the genital area is very sensitive to chemical irritants such as soaps, deodorants, sanitary pads, tight clothing, or synthetic underwear.
These irritants can cause eczema or dermatitis, leading to persistent itching and burning.
5. Yeast infection
Most women experience a vaginal yeast infection (candidiasis) at least once, caused by the overgrowth of Candida fungus.
Normally, the vagina maintains a balance between good bacteria and yeast, but when this balance is disturbed, yeast can multiply excessively.
Symptoms include itching or burning, thick white or clear odorless discharge, and irritation in the vaginal area.
1. Poor hygiene
Not changing underwear or sanitary pads regularly can create a moist environment that supports the growth of bacteria and yeast.
2. Sweating
Everyone sweats in the genital area because it contains apocrine glands, similar to those in the armpits. These glands produce thicker sweat than the eccrine glands found elsewhere in the body.
When the proteins in sweat mix with skin bacteria, this interaction can cause unpleasant odors. If sweat dries on the skin, it can also lead to itching in the groin and vulva.
3. Menopause
A decrease in estrogen levels at the end of the reproductive period can cause the vaginal wall to become thinner and drier, resulting in itching and irritation. This can also occur in some breastfeeding women.
How to prevent recurring itching in the intimate area

Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the itching is triggered by an irritant, avoiding it will help ease the symptoms.
You can also take the following steps to prevent recurrence:
- Wear loose, cotton underwear.
- Avoid scented soaps or cleansers. Clean the genital area only with clean water and pH-balanced mild soap.
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Avoid scratching, as it can damage the skin and worsen irritation or cause infection.
- Use panty liners or sanitary pads only during menstruation.
- Change sanitary pads or tampons regularly.
- Avoid vaginal douching.
When to see a doctor
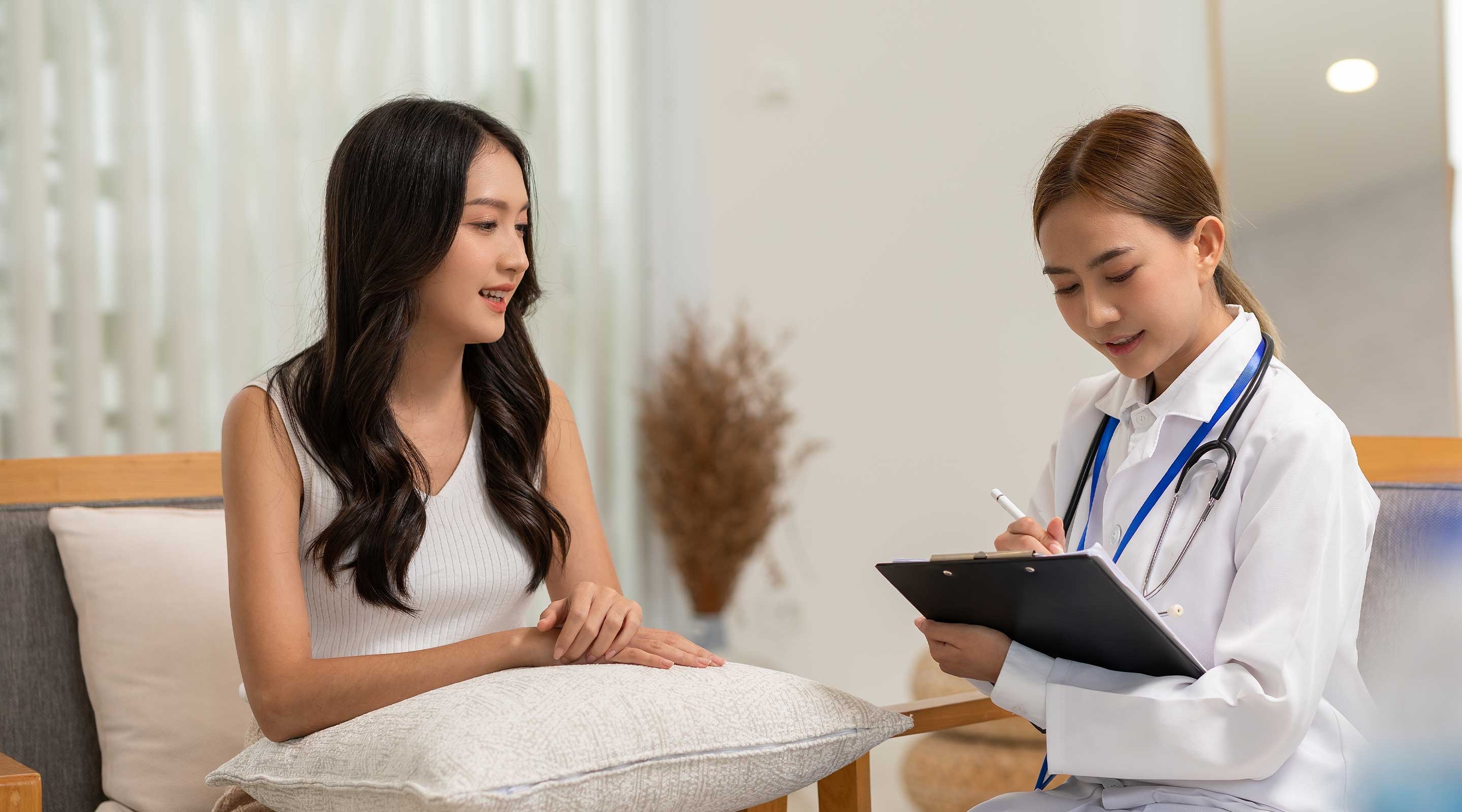

See your doctor if vaginal itching lasts more than a week, becomes severe enough to interfere with daily activities, or is accompanied by:
- Sores or blisters on the vulva
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling in the genital area
- Redness or other color changes in the genital area
- Difficulty urinating
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
If the itching or odor in your intimate area keeps coming back or causes significant discomfort, don’t ignore it.
Consult your doctor to determine the cause and get the right treatment.