Signs of Nutritional Deficiency

Broken nails, hair loss—recognizing the signs that you are deficient in vitamins and minerals can help you adjust your intake.
The body needs vitamins and minerals to stay healthy. Unfortunately, the intake of these nutrients is often not properly absorbed, leading to deficiencies.
When the body lacks essential vitamins or minerals, it will show clear symptoms. Here are six warning signs of vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
1. Severe hair loss and brittle nails
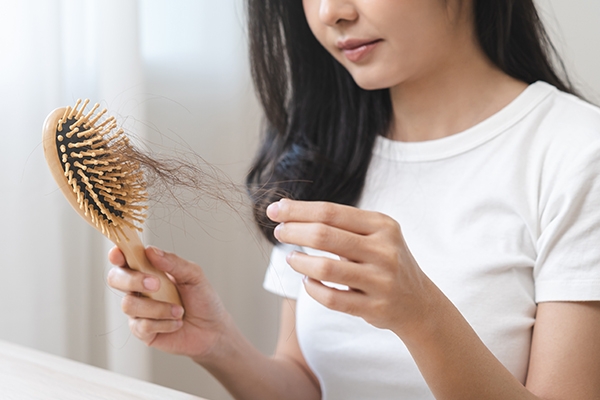

Each person loses about 100 strands of hair per day. However, if you find a clump of hair on your pillow or in the bathroom drain, consult a doctor immediately. This could be a sign of a problem.
Severe hair loss may signal low iron levels. Other signs of iron deficiency include weakness and fatigue, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, pale skin, headaches, cold hands and feet, a sore or swollen tongue, and brittle nails.
Tips
- Paying attention to your diet can help you improve your iron levels. Iron-rich foods, like red meat, green leafy vegetables like spinach, mustard greens, broccoli, and nuts. Supplements may also be helpful if needed.
- Adult women over 18 require 18 mg of iron daily, while men need 9 mg. Teenagers over 12 years old typically need 11-15 mg.
2. Swollen and numb tongue

Symptoms of severe vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, pale skin, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty thinking and remembering, and visual disturbances.
Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining healthy neurons and blood cells. It also assists the body in producing DNA, the genetic material found in all cells. Our bodies do not produce vitamin B12 on their own. To obtain vitamin B12, you must consume meals and beverages containing it.
Tips
- Vitamin B12 can only be found in animal foods, including meat, liver, fish, eggs, and milk. The intake of vitamin B12 varies from person to person.
- Adults need 2,000 mcg per day, whereas children need 1,000 mcg per day or once every two weeks.
3. Wounds are hard to heal
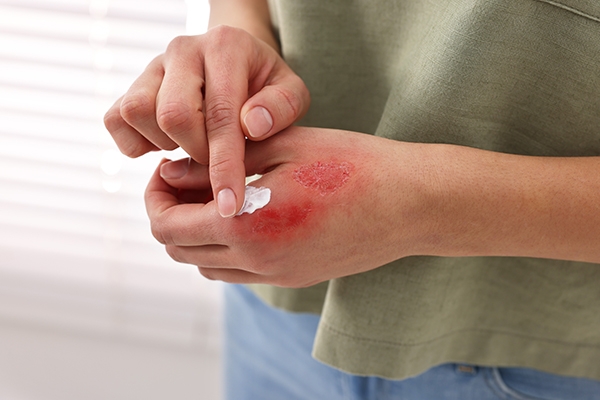

If your gums are red, swollen, and bleeding, you may need to increase your vitamin C intake. Another indication is that you bruise easily.
Vitamin C promotes cell repair and wound healing. It also acts as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant, helping to reduce cell damage.
Vitamin C affects the body's tissue repair and regeneration. Vitamin C produces collagen which aids wound healing. Vitamin C reduces inflammatory reactions in gum disease and the structures around the teeth.
Tips
- First and foremost: If you smoke, quit. Smoking reduces the body's ability to absorb vitamin C.
- Consume more fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C, including kiwi, tomatoes, red peppers, broccoli, strawberries, and oranges. Adults need 75–90 mg of vitamin C daily.
4. Joint pain
Vitamin D deficiency can cause bone pain, brittle teeth, immune disorders, and even depression.
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in helping the body absorb essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, which are vital for maintaining bone health. It also helps regulate calcium levels in both the bones and the blood.
If you do not get enough vitamin D, your calcium levels may drop, prompting your body to pull calcium from the bones and transport it into the bloodstream.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency can include muscle weakness and pain, joint pain, muscle cramps, and bone damage, which is often referred to as osteoporosis.
Tips
- Adults need 600 IU (800 IU for those over 70).
- Eat vitamin D-rich food such as salmon, herring, and sardines; cow's milk, soy milk, orange juice, oatmeal, and cereals fortified with vitamin D.
- Sunbathing for 10-30 minutes daily can boost vitamin D levels. Don't forget to use sunscreen. Please note, that 80% of vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight.
5. Muscle cramps and tingling lips
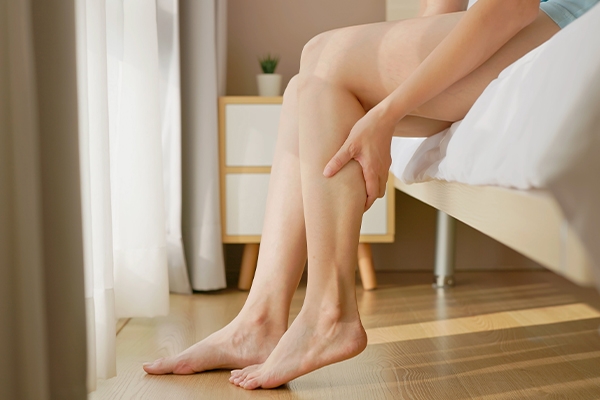

Calcium is important for strong bones and managing muscle and nerve function. Mild to moderate calcium lack includes muscle cramps, tingling lips, dry skin, brittle nails, and hypocalcemia related to vitamin D deficiency.
Tips
Meet your daily calcium needs:
- Children aged 9-18 need 1,300 mg to support optimal bone growth.
- Adults aged 19–50, and men aged 51–70 need 1,000 mg daily
- Women over 51 or who have reached menopause need 1,200 mg. This is because of the decrease in estrogen levels, which can cause bone fragility if not balanced with sufficient calcium intake.
- Men and women over 70 years old need 1,200 mg to maintain their bone health.
Calcium-rich foods including milk and dairy products like cheese and yogurt, are good sources of calcium. If you are not a big fan of milk or are on a vegetarian diet, you can find calcium in dark green leafy vegetables like kale and broccoli, almonds, whole grains, and plant-based milk.
6. Night blindness

Vitamin A deficiency can cause vision problems. One of them is night blindness, which is a reduced ability to see in dim light or dark.
Vitamin A has two important roles in the human eye. Vitamin A is needed for the normal functioning of the visual system and to maintain the integrity of epithelial cells. In the retina, vitamin A is a precursor to photopigments, which play a vital function in the visual system.
Vitamin A is needed to produce rhodopsin, a protein in the retina that plays a role in the eye's adaptation to light, especially from bright to dark places. Vitamin A is also important in maintaining the structure of the conjunctival and corneal epithelium.
Eye disorders that can be found due to vitamin A deficiency are xerophthalmia, which can damage the cornea and eventually cause blindness. The first symptoms of xerophthalmia are dryness of the conjunctiva, then Bitot's spots, which are whitish deposits that appear on the conjunctiva of the eye (the clear layer on the outside of the eye).
Tips
- Our bodies cannot produce vitamin A on their own, therefore eating vitamin A levels is through consumption of foods rich in vitamin A. Diets high in vitamin A include milk, eggs, fish, offal, and green leafy vegetables.
- Adult men require 700 mcg of vitamins per day, whereas adult women need 600 mcg.
**
For most healthy adults, the best way to avoid or treat nutritional deficiencies is to ensure that you eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet. A blood test can determine the vitamin and mineral levels in your body.
However, routine blood tests at an annual physical exam usually do not include most of these tests. Therefore, having a medical checkup (MCU) is an important step to assess your overall health.
If you’re looking to consult with a healthcare professional or do a medical checkup, visit the GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta. Our team of doctors is ready to help you do tests that meet your health needs. Don't delay; start taking care of your health today!



