Rabies: Death from a Little Bite

Throughout 2023, 47 people died from rabies." Data from the Ministry of Health of Indonesia for 2023. In Indonesia, the rabies fatality rate is around 100%. This is an outbreak.
Rabies incidents in Indonesia surged dramatically between January and June 2023. Rabies is not a new threat. It's been there for a long time. It was revived when a youngster in NTT died after being bitten by a rabid dog. Similar instances occurred in Bali.
There were 300 rabies cases, four of which died, making Bali the region with the most rabies cases in Indonesia. Just eight provinces in Indonesia, namely the Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung, DKI Jakarta, Central Java, Yogyakarta, East Java, West Papua, and Papua, have been proclaimed rabies-free.
Rabid dogs are responsible for 95% of all rabies incidents. Apart from dogs, cats, monkeys, bats, ferrets, and even rabbits can transmit rabies, albeit in considerably lower numbers than dogs.
The rabies virus belongs to the Lyssavirus genus. This virus is found in the mouth, particularly in the saliva. The virus enters the human body through bites, scratches, or licks on wounds on the skin and eventually ends up in the central nervous system or the brain. Cases of rabies without bites are uncommon.
The virus can also enter the human body by direct contact with the mucosa of the eyes, mouth, and open wounds, where it can end up in the brain or central nervous system. This is what causes rabies cases to be fatal (100%). Rabies cases that do not involve bites are rare.
How is it then transmitted? Rabies can be spread in three ways: between animals, animals and humans, and, in rare situations, between humans and humans.
Which animals can cause rabies? Most cases come from unvaccinated dogs and cats, livestock, and horses. In Australia and Western Europe, rabies transmitted by bats is an emerging infectious disease. In addition, raccoons, skunks, foxes, and other wild animals can also cause rabies, although cases are rare.
What are the symptoms in humans?
Infection is followed by an incubation period of 30-90 days. It then continues to the prodromal phase, during which symptoms occur (2-10 days). Symptoms of rabies include fever, weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, sleeplessness, severe headache, sore throat, and discomfort.
Following the appearance of these symptoms, there will be an acute neurological period (2-10 days), with symptoms such as a burning or tingling sensation at the bite site, anxiety, and the onset of phobias such as hydrophobia, aerophobia, or photophobia. Typically, the sufferer is not saved after experiencing these varied symptoms.
If you have been bitten by one of those animals, immediately undertake the following: First, wash the bite marks in running water for at least 15 minutes with soap or detergent.
Second, an antiseptic, such as 70% alcohol, should be applied to the wound. Keep the wound open. Third, receive an anti-rabies vaccination (ARV) or anti-rabies serum (ARS) from a health center.
Ideally, within the first 24-48 hours of exposure. You will require a second dose seven days later if you have already received a rabies vaccination.
If you have never been immunized, you must obtain an extra dosage on days 3, 7, and 14. When you have your first dose of vaccine, you'll also require an injection of rabies immunoglobulin (rabies antibody).
The doctor will determine the severity of the wound during the examination.
- Low: skin licks or touches.
- Moderate: bites or scratches, but no injuries.
- High: bites, licks, or scratches that cause open, bleeding wounds.
After determining the type of wound, the doctor conducts a series of tests:
- Antibody test to evaluate viral immunity.
- A CT scan or MRI to identify whether the virus causes brain inflammation.
- A biopsy if there is an open wound.
- Rabies virus culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to determine whether animal saliva is in the wound.
The death occurred as a result of the delay in getting the victim to a medical facility, mainly because they believed they only received little bites and did not bleed.
New victims were brought in after one month or when they showed symptoms. The victim may be spared if treated promptly and given an anti-rabies vaccination.
Rabies animal detection
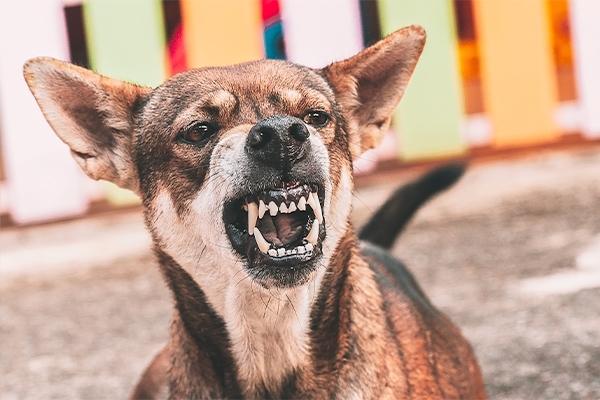

Rabid animals typically exhibit symptoms such as becoming vicious, not obeying the owner's orders, being unable to swallow, being paralyzed, having an open mouth and excessive salivation, hiding in cool and dark places, having their tails curved under the stomach between the two legs and thighs, convulsions, and eventually death. Asymptomatic rabies, on the other hand, might cause sudden death.
How can we avoid it?
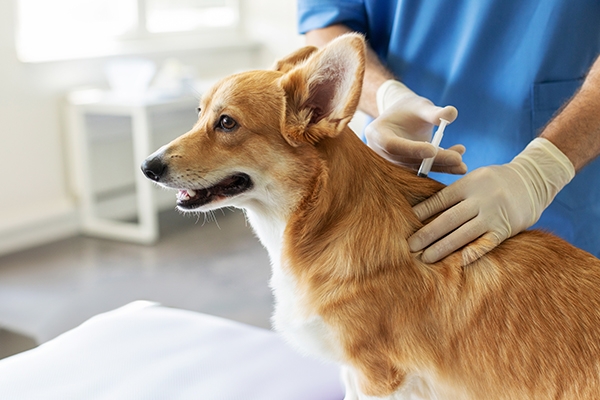
Rabies can be avoided by immunizing pets with ARV once a year. Forbid them to roam because a single bite from a rabid animal can infect your pet. If your dog, cat, or other mammalian pet exhibits unusual behavior, immediately take them to the clinic.
Vaccination is a critical step in rabies control. Avoid extreme actions against them, such as torturing or killing them.
Rabies is a lethal illness that almost always causes death. It is, however, fully avoidable if treated promptly. If an animal has ever bitten you or you worry you have rabies, visit GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta, to get the treatment and vaccination.



