Leukemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments You Should Know

The cause of leukemia, also called blood cancer, is often unknown. It is caused by an increase in white blood cells in the body.
Leukemia develops when a cell's DNA in the bone marrow changes (mutates) and cannot grow and function normally.
Leukemia cells frequently act like abnormal white blood cells. Treatment depends on the type of leukemia suffered, age, and overall health condition. It is also influenced by whether the disease has spread to other organs or tissues.
Unlike other cancers, leukemia does not form a mass (tumor) visible on imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans.
According to Global Cancer Statistics, 474,519 new cases of leukemia were diagnosed in 2020, with 311,594 deaths from leukemia worldwide. The most common cases were found in Asian countries.
The most common type of leukemia is chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It usually attacks adults aged 55 years and up.
Cases in children are almost non-existent. In Indonesia, leukemia is the fifth most prevalent cancer, with the highest number of deaths after lung, breast, cervical, and liver cancers. It affects men more than women. According to WHO data, there were 11,314 deaths from leukemia in Indonesia in 2019.
Leukemia symptoms
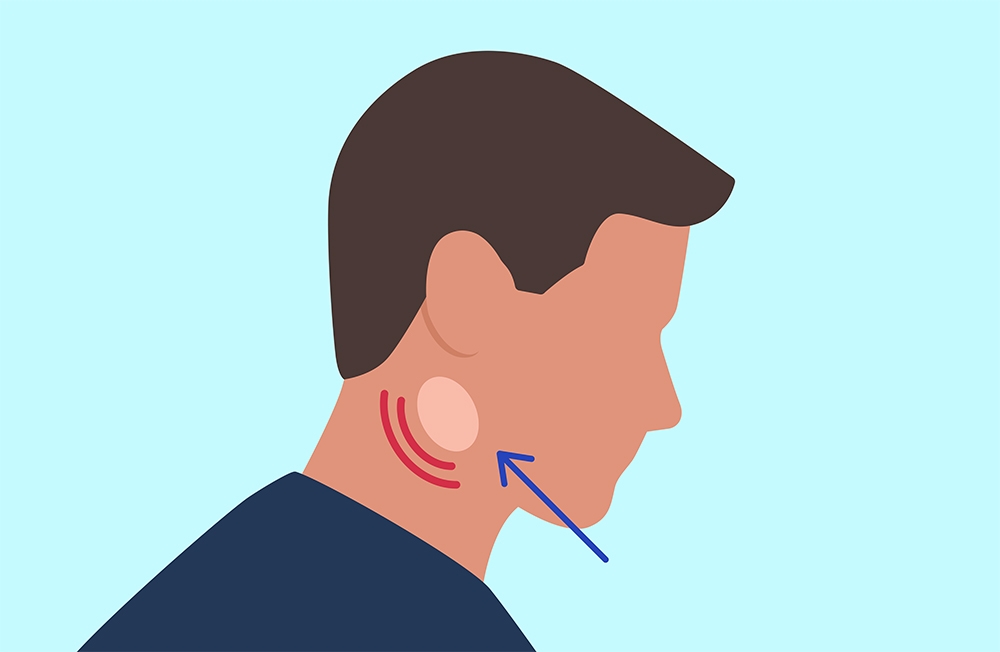
Leukemia symptoms can vary depending on the type. Some common signs to look out for include:
1. Easy bruising or bleeding
Leukemia damages the platelets in the body, making it difficult for the blood to clot. Some people with leukemia may experience:
- frequent bruising with no apparent reason
- minor cuts that take a long time to heal
- nosebleeds or bleeding gums
- small red spots on the skin
- purpura (purple spots on the skin)
2. Frequent infections
White blood cells are critical for fighting infections. If they do not function properly, a person may experience frequent infections, and the immune system can attack its cells.
3. Anemia
Anemia can develop when the number of effective red blood cells decreases due to reduced hemoglobin levels in the blood.
Anemia symptoms include frequent dizziness and fainting, lethargy, fatigue, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, easy stiffness, and a pale face.
4. Painless swelling of the lymph nodes (especially in the neck and armpits).
5. An enlarged liver or spleen.
6. Other symptoms include nausea, fever or chills, bone pain, fatigue that doesn't improve with rest, weight loss, and night sweats.
Leukemia risk factors
Anyone can get leukemia. However, research suggests that certain factors may increase your risk, including:
1. History of cancer treatment
Past cancer treatment involving radiation or chemotherapy can increase your chance of developing some types of leukemia.
2. Smoking
If you have a history of smoking or are exposed to secondhand smoke, you are at higher risk of developing acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
3. Exposure to industrial chemicals
Benzene and formaldehyde are known cancer-causing chemicals in building materials and household products. it is used to create plastics, rubber, dyes, pesticides, medicines, and detergents.
Formaldehyde can be found in building materials and household products, such as soaps, shampoos, and cleaning products.
4. Certain genetic disorders
Genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis, Klinefelter syndrome, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, and Down syndrome, may raise the risk.
5. Family history
Research suggests that some types of leukemia may run in families. But in most cases, having a relative with leukemia does not mean that you or another family member will have leukemia.
6. Viral infections
Infection with Epstein-Barr virus, a human T-cell lymphotropic virus, may increase the risk of developing leukemia.
Types of leukemia

Acute leukemia occurs quickly and becomes severe in a short period, while chronic leukemia progresses slowly and slowly.
There are four most common types of leukemia. The type of cancer is determined by how quickly it spreads and which white blood cells are impacted.
AML
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common kind of leukemia among adults. It spreads quickly and affects the blood and bone marrow. Treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplantation.
ALL
Acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL) grows rapidly and can affect blood marrow throughout the body.
ALL can spread to the liver, spleen, or lymph nodes. It most often occurs in children under 15 or adults over 45. ALL accounts for the majority of leukemia diagnoses in children under 15 but is rare in adults.
CLL
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) primarily affects elderly people and accounts for one-third of all leukemia diagnoses.
Its incidence is very close to AML. Some kinds of CLL begin slowly, and symptoms may not appear for years, while other forms of CLL multiply.
HCL
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare form of CLL. It develops gradually and is most common in middle-aged or older people. HCL is a chronic disease.
CML
Only 10% of leukemias are chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It is more common in adults than children, and it can go from slowly progressing to rapidly growing.
Unlike other types of leukemia, CML is linked with an abnormal chromosome known as the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph chromosome). It can gradually spread to different parts of the body.
Leukemia treatment
Leukemia treatment depends on many factors. Your doctor will select leukemia treatment options based on your age and health, the type of leukemia, and how far it has spread in your body, including your central nervous system.
Your doctor will recommend leukemia treatments, such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplantation, and immunotherapy.
**
Leukemia is a blood cancer that can develop quickly or slowly, depending on the type. Although the specific etiology is unknown, several risk factors, such as exposure to chemicals, smoking habits, and family history, might raise a person's chances of getting this disease.
If you experience suspicious symptoms, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection can improve the chances of effective treatment and prolong the life expectancy of leukemia sufferers.
Stay alert and take care of your health!



