How Do You Manage Diabetes If You Have Genetic Risk Factors?

Dina, the mom, is worried about her daughter. Her concerns are not without reason, considering that diabetes has become part of her husband's family including him. The question that haunts Dina is: Will her only daughter also have diabetes like her father?
Diabetes has become a common disease in families. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the number of diabetes cases in Indonesia is increasing rapidly. In 2021, as many as 19.5 million people were diagnosed with diabetes, and this number is projected to reach 28.6 million by 2045. Most of the causes are unhealthy diets.

Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease in which blood glucose (blood sugar) levels exceed normal limits. Random blood sugar levels are considered normal if below 200 mg/dl, while normal fasting blood sugar levels are below 126 mg/dl.
Although unhealthy eating habits are the leading cause, other factors contribute to the emergence of diabetes, such as family history and genetics.
In type 1 diabetes, if one parent has diabetes, the risk of a child having type 1 diabetes is around 6-9%, while if both parents have diabetes, the risk increases to 20-25%.
In type 2 diabetes, if one parent has diabetes, the probability of a child having type 2 diabetes is 30-40%, while if both parents have diabetes, the risk increases to 70-80%.
Genetics do raise your chances of having diabetes, but you still have control over how you avoid and manage it.
The choice is yours. You can either monitor your health and live a healthy lifestyle to reduce your risk, or you can ignore it and continue with the diet and lifestyle that increases your chances of having the disease.
If you choose to form healthy habits, here are some tips.
1. Eat more healthy foods

When we were little, our parents or grandparents always reminded us to eat right. “Don’t eat or drink too many sweets.” It turns out they were correct.
Eating habits do have a significant impact on our general health, for better or worse. Your dietary choices are especially crucial if you have a hereditary predisposition for diabetes. A diabetes diet is a healthy diet that helps control blood sugar levels. So, what should you do?
- Maintain a balanced diet.
- Consume more whole foods and vegetables.
- Control your portions and limit your carbohydrate intake.
- Limit your intake of sugary and processed foods.
2. Exercise regularly
If you are sedentary, there's bad news: a sedentary lifestyle can increase your risk of diabetes, as well as several other chronic conditions, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol issues.
However, exercise can help you stay healthy and prevent or manage diabetes. Research conducted by Harvard Health confirms this, showing that exercise can help with weight control and lower blood pressure, LDL (bad cholesterol), and anxiety. In addition, exercise strengthens muscles and bones and increases HDL (good cholesterol).
Physical activity can help people with diabetes lower blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and fight insulin resistance.
The best time to exercise can vary from person to person. However, try to be active about one to three hours after eating. Do light movement every 30 minutes or so. If you have diabetes or are at risk, consider exercising for two to three hours weekly. You can divide it into four to five days. Remember, running, cycling, swimming, dancing, and brisk walking are exercises!
3. Avoid smoking and alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can both increase the risk of diabetes. Smoking can interfere with insulin function, leading to insulin resistance. Meanwhile, alcohol can disrupt blood sugar levels, making it difficult for the body to control glucose.
4. Be aware of genetic risk
Understanding your genetic predisposition can help you manage and take preventive measures. To understand your hereditary risk for diabetes, consider:
- Genetic testing to understand your genetic predisposition to diabetes.
- Changing your lifestyle to meet your health risks and needs.
- Making family plans to minimize the risk of diabetes in the next generation.
5. Monitoring blood sugar levels
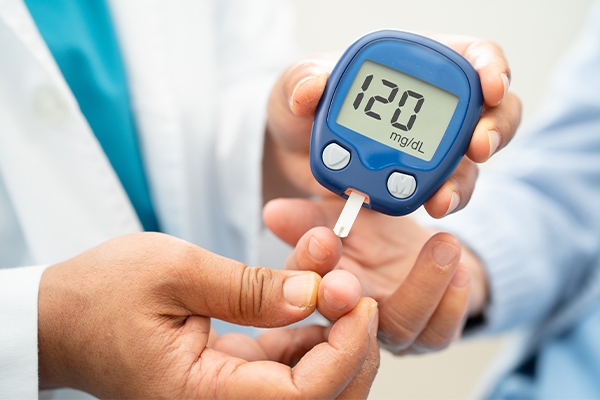
Whether you have a family history of diabetes or not, regular health checks are essential. One of them is checking blood sugar levels. This examination can help detect risk factors early and allow for timely treatment.
Regular check-ups not only help prevent diabetes but also improve its management. As a result, we must plan regular health checks to monitor blood sugar levels.
Remember, we can’t change our genetics. But lifestyle choices can make a big difference. With the right decisions, like adopting a healthy diet and living an active lifestyle, you can significantly lower your risk of diabetes.
6. Keep your blood pressure under control
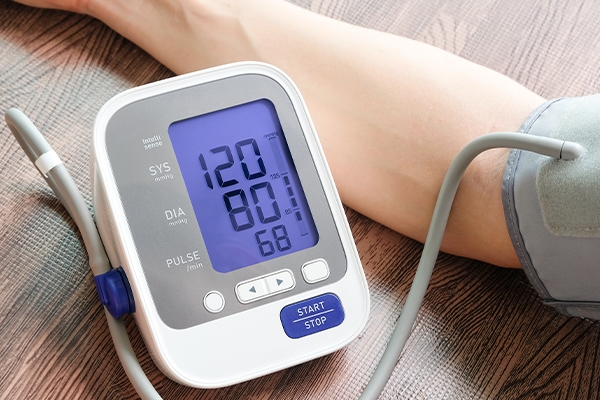
Keeping your blood pressure below 120/80 mmHg is critical regardless of age. Ideal blood pressure can vary as you age, but this is a good starting point. If your blood pressure starts to reach this level, your risk of developing diabetes can increase.
Some of the tips above may not be entirely suitable for children. Mrs. Dina can take the following steps to avoid and manage diabetes since childhood:
- Be active together. Take the children to play outside, walk to the park, take the dog for a walk, or play with siblings. This joint activity can improve children's physical health and be enjoyable.
- Provide nutritious snacks. Choose snacks high in fiber and low in added sugar or refined carbohydrates. Replace processed foods like chips and candy with fresh fruit with peanut butter, vegetables with peanut sauce, smoothies, yogurt parfaits, or whole-wheat pizza.
- Limit your screen time. Set a daily screen time limit, which includes sitting in front of the computer or TV. Encourage your kid to engage in activities like playing outside or making crafts. Make family mealtimes a habit and avoid eating in front of the TV.
Having a family history of diabetes does not necessarily mean that you will develop it. Diabetes develops due to a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental or lifestyle factors that trigger the disease.
Genetic testing can help doctors diagnose more accurately and prescribe the proper treatment based on your diabetes type. If you feel at risk of developing diabetes, consult a team of doctors at GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta, for further examination.
You can visit GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic, to get the necessary treatment and care. Diabetes can be better managed if it is detected early.



