Dengue Fever Test

In rare cases, dengue-hemorrhagic fever can be fatal. The cause is delays in taking action and treating patients. Detecting dengue fever early through a series of tests is one of the measures to prevent the fatal consequences of dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Dengue fever is a disease that spreads through the bite of a mosquito infected with one of the dengue fever viruses. Aedes Aegypti is the main vector. This black and white mosquito likes to lay its eggs in containers filled with clean water, which are typically found in or around the house.
Adult mosquitoes prefer to relax, avoid disturbances, and bite during the day. The peak of biting activity occurs in the morning, 2-3 hours after dawn, and in the afternoon, a few hours before dark.
After being bitten by an infected mosquito, the virus takes 3–14 days to incubate. Mosquito bites cause fever and other non-specific symptoms. Acute fever lasts 2–10 days.
The most common symptoms of dengue fever a high fever, headache, body aches, nausea, and rash. Dengue fever often recovers on its own.
The phases of dengue hemorrhagic fever are divided into three phases. First is the fever phase (febrile). It usually lasts seven days. For 1–3 days, the people will usually experience a high fever. Second, there is the critical phase. This phase lasts approximately two days, starting on days 4–5. In this phase, they feel that the fever has gone down. And the third phase is recovery. In this phase, they will feel their fever rise again (3-5 days after the critical phase). Platelets began to increase and returned to normal.
Severe dengue fever can cause shock, internal bleeding, and even death. Having suffered from dengue fever, being pregnant, or being a baby are some things that can increase the severity.
If you have a fever and experience any of the following signs, seek immediate medical attention:
- belly pain, tenderness
- vomiting more than three times in 24 hours
- bleeding from the nose or gums
- vomiting blood, or blood in the stool
- feeling tired, restless, or irritable
Dengue fever can be treated at home. To treat symptoms, the doctor will usually prescribe numerous medicines to reduce the symptoms until they fully recover. There is no specific medicine for dengue fever.
Drinking enough water is also recommended to prevent dehydration. However, avoiding mosquito bites is the best way to avoid this disease.
What tests should be done?
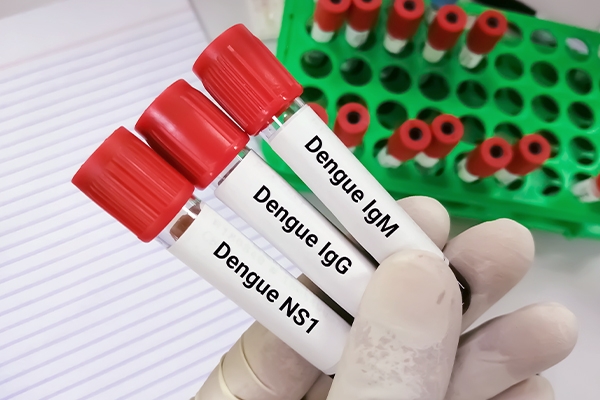
Dengue fever can be diagnosed with a blood test. Blood samples are collected from a vein in the arm area.
The following tests must be done to identify the dengue virus in fever.
1. A complete blood check
Complete blood tests, including platelets, plasma, and hematocrit. Note trends in hematocrit, leukocytes, and thrombocytes. A person who is suspected of having dengue fever has a hematocrit that rises >20%, leukocytes <5000 microliters, and platelets approaching 100,000 or <100,000 microliters.
2. Dengue NS1
This test detects the NS1 protein found in the dengue virus. The test is carried out 0–7 days after dengue fever symptoms appear. This test is not recommended for people with fever symptoms for more than 7 days.
3. Serology
It is useful for detecting IgG and IgM antibodies produced by the immune system after being exposed to the dengue virus. An effective test is conducted at least four days following the onset of symptoms.
4. SGOT and SGPT to determine liver function abnormalities.
Home fever test
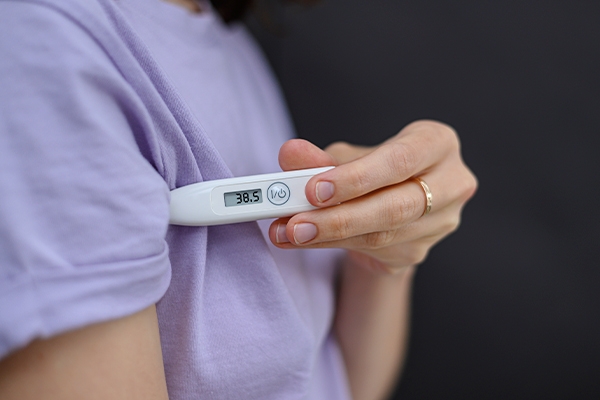
A thermometer is a test tool that must be available at home. This tool is considered accurate for measuring body temperature. However, what if there is no thermometer available, even though we need to check body temperature? Don't worry! Do the following:
1. Touching the forehead
Touching the forehead with the back of the hand is a common way to find out whether someone has a fever or not. If the people have a fever, their forehead may feel quite hot.
It may not be accurate, but it can provide some general information.
2. Pinching the back of the hand
Dehydration can be an indication of fever. To check whether someone is dehydrated or not, you can gently pinch the skin on the back of their hand, then remove it and look at it carefully.
If the skin is well hydrated, it will return to its original condition very quickly. If the skin moves slowly, it may be dehydrated. However, this method can also be inaccurate because dehydration does not always indicate a fever.
3. Checking the cheeks
A person who has a fever usually has reddish or purple cheeks.
4. Check urine conditions
Changes in the color, frequency, or volume of urine may indicate a fever. When you have a fever, your body is dehydrated, so your urine becomes more concentrated, dark yellow or orange, and may even have an odor.
Dengue fever vaccine

Vaccination is another way to help avoid dengue disease. The Indonesian Pediatrician Association and the Indonesian Association of Internal Medicine Doctors have recommended the dengue fever vaccine for child immunization in 2023.
Tetravalent vaccines prevent dengue fever caused by four virus serotypes: DENV 1, DENV 2, DENV 3, and DENV 4. This vaccine contains a weakened dengue virus and does not cause disease. Tetravalent vaccines are approved use for in children and adults from 6 to 45 years old.
Vaccines are usually given in two doses, three months apart, and administered by subcutaneous injection into the upper arm muscle.
If you have any of the symptoms above or would like to get dengue fever vaccination services, please click WhatsApp.



