Why Should Children Get the Hepatitis Vaccine? Here’s the Explanation

As parents, we want our children to grow up healthy without facing serious illnesses. One condition to be aware of is hepatitis, which is liver inflammation that can affect children from an early age.
The problem is, hepatitis often shows no obvious symptoms in the beginning, so it is usually detected only when the condition has already become severe.
The good news is that hepatitis can actually be prevented. One of the most effective ways is by giving children the hepatitis vaccine starting from infancy.
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver that can affect anyone, including children.
In children, the most common cause is a viral hepatitis infection. If left untreated, hepatitis can lead to long-term liver damage and may even progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer later in life.
Depending on its course, hepatitis can be:
- Acute: sudden onset, short-term, and may completely heal.
- Chronic: long-lasting, with a risk of permanent liver damage.
Types of hepatitis common in Children
There are five types of hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, and E). However, the ones most often seen in children are hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is spread through contaminated food or drinks, such as unclean water or improperly washed food.
Although hepatitis A is highly contagious among children, the risk of liver damage is very low. The illness is generally mild and can completely resolve in less than six months.
Globally, there are about 1.4 million new hepatitis A cases every year. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), children are more likely to be infected with hepatitis A, especially those living in areas with poor sanitation.
The incubation period for hepatitis A is 15–50 days after infection, with an average of about 28 days. Diagnosis can be confirmed through a blood test for IgM anti-HAV.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B cases are very common in Indonesia, making vaccination from birth an important step to protect children. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Indonesia ranks first in Southeast Asia for hepatitis B cases.
Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood, needles, bodily fluids, or from mother to baby during childbirth.
This infection can become chronic and last a lifetime. Over time, it may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Symptoms of hepatitis in children
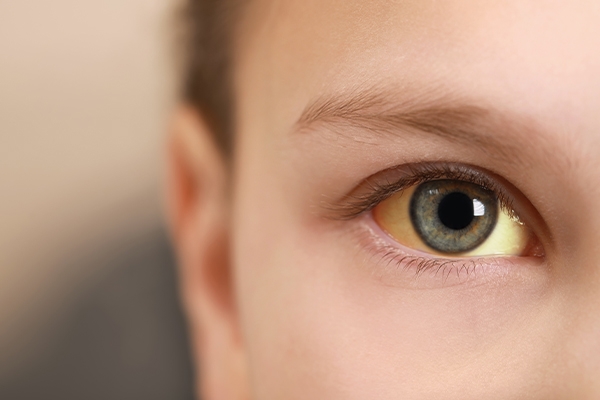

Symptoms of hepatitis may vary, but common ones include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Nausea or vomiting
However, not all children show clear symptoms, which is why vaccination is much safer than waiting until illness occurs.
How to prevent hepatitis in children
1. Hepatitis vaccination
The Indonesian Pediatric Society (IDAI) recommends:
- Hepatitis A: given after the age of 2 years, in 2 doses spaced 6–12 months apart.
- Hepatitis B: given from birth (4 doses: at birth, 2 months, 4 months, and 6 months), with a booster at 18 months.
If a baby is seriously ill, vaccination should be postponed until recovery, and catch-up immunization can be done afterwards.
Vaccination is the best protection, as it prevents infection before the virus can cause disease.
2. Maintaining food and water hygiene
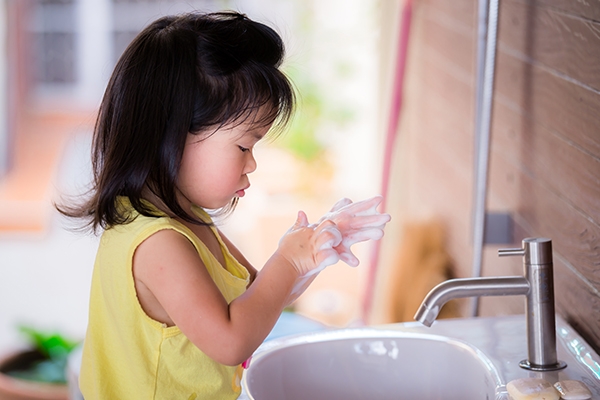

- Teach children to wash their hands with soap for at least 20 seconds before meals.
- Parents and caregivers should also practice proper hand hygiene when preparing food.
- Avoid sharing eating utensils and ensure drinking water is clean.
3. Hygiene at home and childcare centers
- Make sure caregivers or childcare facilities maintain cleanliness, especially when changing diapers or preparing food.
- Keep medicines out of children’s reach.
4. When traveling
- Consult a pediatrician before traveling to areas with a high risk of hepatitis.
- The doctor may recommend additional vaccines, particularly hepatitis A.
**
Hepatitis can be prevented through simple steps, especially by ensuring early vaccination. By giving hepatitis A and B vaccines on schedule, parents provide lifelong protection against serious liver diseases.
Combined with good hygiene practices for food and the environment, the risk of hepatitis in children can be significantly reduced.
Give your little one the best start in life with complete hepatitis vaccination. Visit GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta, for safe, trusted, and doctor-supervised immunization.



