6 Diseases That Often Attack Children and How to Treat Them

Be aware of common diseases that affect children. Recognize the symptoms, causes, and the right way to treat them so your little one stays healthy and happy.
Children's immune systems are weaker than adults', making them more ill-prone from fever and diarrhea to respiratory and urinary tract infections. These diseases can strike at any time, especially during the transitional season.
Here are some common childhood diseases, their symptoms, and how parents can treat them.
Fever

Fever is the body's natural response to fighting infection. A child is reported to have a fever if his/her body temperature exceeds 38 degrees Celsius.
Generally, fever is caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Although it worries parents, fever is not always a sign of danger. In fact, it can be a sign that the child's immune system is working.
To manage fever, apply a warm compress to the forehead or armpit, drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, and rest.
Pneumonia

Pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under five years old. According to WHO data in 2021 shows that every year, around 740,000 children die from this disease. In various parts of the world, a child dies from pneumonia every minute.
Pneumonia is an acute infection of the lungs caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. In toddlers, the most common or frequent symptoms are coughing, shortness of breath, and signs of acute pneumonia, such as pulling the lower chest wall inward when breathing.
Preventive measures include complete immunization (especially the PCV vaccine), environmental hygiene, and maintaining children's nutrition to have strong immunity.
Diarrhea

Diarrhea can cause rapid fluid loss and can lead to severe dehydration. This disease is caused by infections of viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
Diarrhea is characterized by loose, watery stools and frequent bowel movements. If not appropriately treated, diarrhea can lead to dehydration. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diarrhea is the leading cause of death in children worldwide.
This disease can heal on its own within 1-2 days. If it does not heal within that time, there may be a problem with the child.
Treatment will depend on the child's symptoms, age, general health, and the cause and severity of the condition.
Children with diarrhea should drink plenty of fluids. This helps replace lost body fluids. If your child is dehydrated:
- Give them a drink made from a glucose-electrolyte solution. This solution consists of water, sugar, and salt in the right proportions.
- Avoid juice, soda, and other sugary drinks.
- Do not give them too much water, especially to babies.
- Keep breastfeeding your baby to maintain fluid and nutrient intake.
- See a doctor immediately if your child shows signs of severe dehydration, such as dry lips, crying without tears, weakness, and infrequent urination.
Urinary tract infection (UTI)

UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and cause an infection. One of the most common bacteria that causes UTIs is E. coli. This bacteria that originates from the anus can spread to the urinary tract due to poor hygiene or incorrect wiping methods.
Girls are more susceptible to UTIs because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus. Incorrect wiping habits or poor hygiene can be the primary triggers.
Children who experience UTIs usually have symptoms such as fever and chills, pain when urinating, abdominal pain, frequent urination, and cloudy and foul-smelling urine.
Teaching children to wipe properly (from front to back), getting children used to drinking lots of water, and reminding children not to hold their urine are some ways that can be done to prevent children from getting UTIs.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
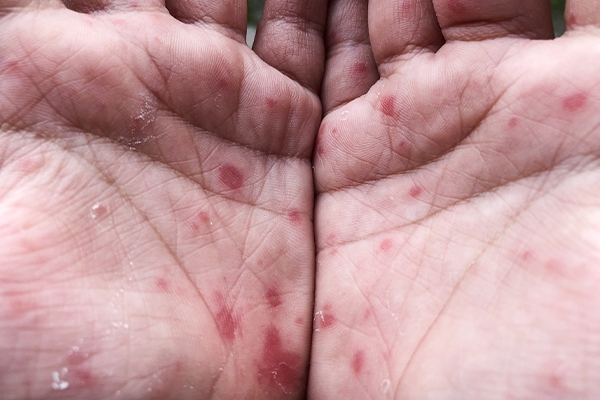

This disease is known as Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD) or Singapore flu. It is caused by several types of viruses, one of the most common being the Coxsackie A16 virus.
It is highly contagious and generally attacks children under five years of age. This disease is characterized by blisters in the mouth, rashes, and red spots on the hands and feet.
1-2 days after the fever, blisters, like reddish canker sores, will appear on the tongue, gums, and inner cheeks. Skin rashes also appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash can also appear on the knees, elbows, buttocks, or genital area.
Although the rash of this disease is often similar to chickenpox, the location of the chickenpox rash usually starts from the chest or back and then to the hands or feet.
Ear infections
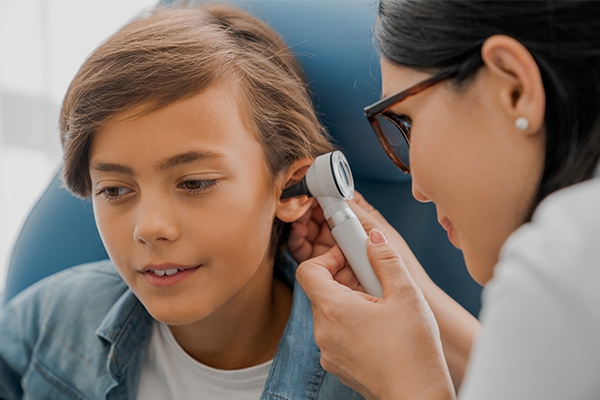
Children often have ear infections, specifically otitis media. This infection occurs in the middle ear, especially the eustachian tube, which connects the ear, nose, and throat.
Symptoms include fever, ear pain, difficulty hearing and sleeping, and ear discharge.
If your child exhibits any of the symptoms listed above, take your child to the doctor to get the right treatment and medication.