Children Are Vulnerable to TB Infection: Recognize the Symptoms!

Rani, a young mother in Jakarta, noticed her 5-year-old son frequently experiencing a fever and losing appetite. She thought it was just a common cold. However, when her son's weight did not increase for two months, and a lump appeared on his neck, she realized that there was something more serious.
The health center diagnosed him with TB. Rani was surprised. "Isn't TB an adult disease?" Children are also very susceptible to TB. Let's learn the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods so our children stay healthy and protected.
**
Based on the Global TB Report 2023, Indonesia ranks second in the world in the number of Tuberculosis (TB) cases, with 1,060,000 new cases and 134,000 deaths each year. This figure reflects the importance of awareness and early detection, especially for children with lower immune systems.
Through the Ministry of Health, the Indonesian government is targeting the detection of 1 million TB cases by 2025, including in children, as a step towards eliminating TB. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are essential in preventing children from suffering the long-term effects of the disease.
Read more: Does Your Cough Indicate TB?
How does TB affect children?
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which spreads through the air via coughs or sneezes from infected individuals.
This bacterium thrives in damp places, especially with poor sanitation and ventilation. However, TB is not transmitted through contact with personal items, such as clothing or eating utensils.
Children are susceptible to infection because their immune systems are not as strong as those of adults. Many have latent TB, where the bacteria remain inactive but can become active at any time if the immune system weakens.
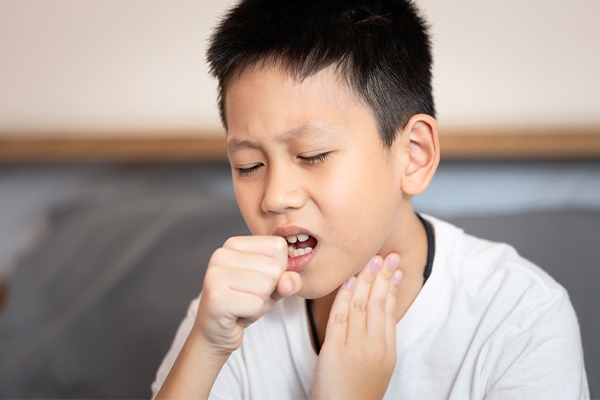
Symptoms of TB in children: don't take it lightly!

Back to Rani's story, if she didn't immediately take her child to the doctor, the TB infection could have spread more widely. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the symptoms of TB in children early on:
- fever for more than two weeks or fever that often recurs;
- sweating at night without cause;
- coughing that persists for more than three weeks;
- the child appears weak, inactive in playing;
- weight stagnation for two months;
- lumps in the neck, armpits, or groin.
TB affects the lungs, meninges, intestines, bones, kidneys, and skin.
How is TB diagnosed in children?
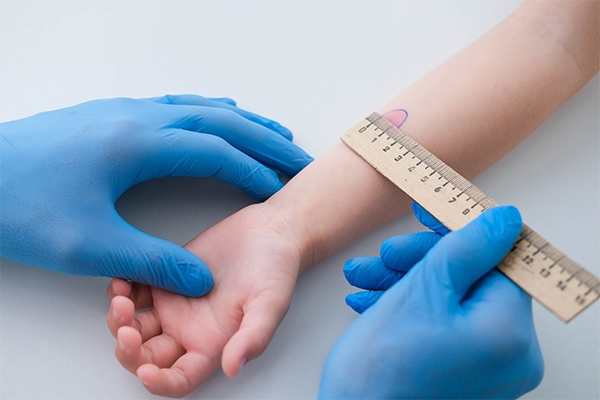
Diagnosing TB in children is more challenging than in adults, who can be examined using sputum. Standard examinations include:
- The Mantoux test: Injecting test material into the skin, the results can be seen from the size of the lump that forms within 48-72 hours.
- Chest X-ray: Determining the condition of the lungs.
- TB blood test: Taking a blood sample to detect infection.
This test is recommended if the child has been in contact with a TB sufferer in the last 5 years, has symptoms of TB, or the X-ray results are suspicious.
TB treatment for children: can be cured if disciplined
- For latent TB, children who are 2 years old and above may be treated once weekly for 12 weeks or daily for several months.
- For active TB, a combination of two to four medications is needed for at least six months.
- Children frequently improve within a few weeks after treatment begins.
Preventive measures
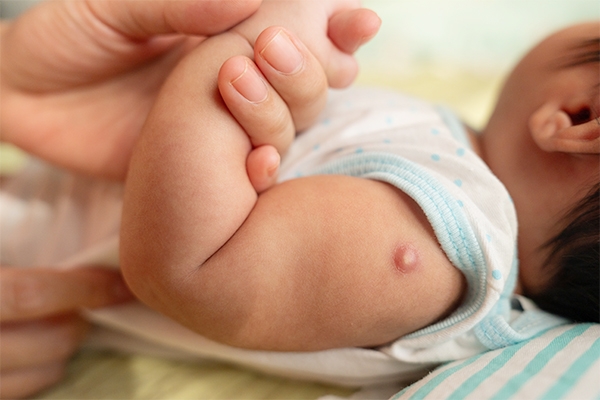
It is better to prevent than to cure. Here's how to protect your little one from TB:
- BCG immunization: Given to newborns up to three months old. If not, administer a Mantoux test to determine whether the child has been exposed.
- Nutritious nutrition: Increases the body's resistance so it is not easily sick.
- Clean and bright environment: A house with plenty of sunlight and no humidity helps prevent the growth of bacteria.
If detected early, TB in children can be prevented and cured. Parents play a vital part in recognizing symptoms, ensuring their children get vaccinations, and maintaining a healthy environment.
To receive a BCG vaccination, visit GWS Medika Clinic, a health clinic in Jakarta, and protect your child’s future from the threat of TB through early detection and effective prevention!



